To help you quickly understand the application fields of various types of tungsten carbide, we have a detailed grade table. If you are interested, please feel free to contact us via email at services@carbidelink.com. Our professional team will be delighted to serve you.
Classification and Functions of Tungsten Carbide in Different Fields
Tungsten carbide, a metallic hard – alloy made via powder metallurgy from refractory – metal compounds and a binder metal, comes in diverse types. It meets complex working – condition demands like cutting, wear, and impact resistance, seeing wide use in production. Its properties—high hardness, wear resistance, strength, toughness, heat and corrosion resistance—stand out; it retains hardness and wear – resistance at 500 °C, and high hardness at 1000 °C. Broadly, it falls into three main categories: for cutting tools, geological and mining tools, and wear – resistant parts.
I. For Cutting Tools
Tungsten carbide for cutting tools is classified into six types—P, M, K, N, S, and H—based on applications:
- P – type: TiC and WC alloy or coated alloy, with Co (or Ni + Mo, Ni + Co) binder, for long – chip materials like steel. P10 suits high – speed, medium – small chip cross – section operations such as turning and milling.
- M – type: WC – based alloy with Co binder and added TiC, for materials like stainless steel. M01 is ideal for high – speed, light – load finish turning and boring.
- K – type: WC matrix alloy with Co binder and TaC/NbC, for short – chip materials like cast iron.
- N – type: WC alloy with Co binder and TaC/NbC/CrC, for non – ferrous and non – metallic materials such as aluminum and plastics.
- S – type: WC matrix alloy with Co binder and TaC/NbC/TiC, for heat – resistant and high – quality alloys like heat – resistant steel.
- H – type: WC matrix alloy with Co binder and TaC/NbC/TiC, for hard – cutting materials like hardened steel.
II. For Geological and Mining Tools
Tungsten carbide for geological and mining tools can be classified into the following categories according to the usage parts:
- A: For rock – drilling bits: For example, the GA05 – grade product is suitable for soft or medium – hard rocks with a uniaxial compressive strength of less than 60 MPa; the GA50/GA60 – grade products are suitable for hard or extremely hard rocks with a uniaxial compressive strength greater than 200 MPa. As the grade number increases, its wear resistance gradually decreases, while its toughness gradually increases.
- B: For geological exploration
- C: For coal mining
- D: For mining and oil – field drill bits
- E: For composite – sheet substrates
- F: For snow – plowing blades
- W: For excavating teeth
- Z: Other types
The Rockwell hardness of this type of alloy can reach HRA85 and above, and the flexural strength is generally above 1800 MPa.
III. For Wear – Resistant Parts
Wear – resistant parts are classified according to the application fields as follows:
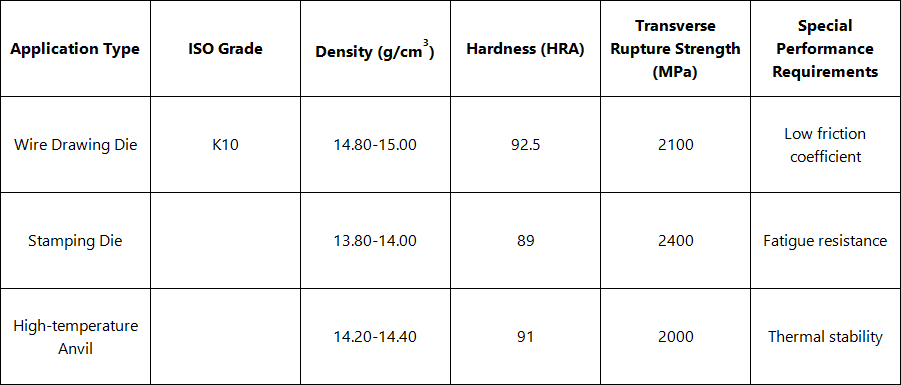
- S: For drawing metal wires, rods, and tubes: Common applications include drawing dies, sealing rings, etc.
- T: For stamping dies: Such as dies used for fastener stamping and steel – ball stamping.
- Q: For high – temperature and high – pressure components: For example, the anvils and pressure cylinders used in artificial diamond synthesis.
- V: For wire – rolling roll rings: For example, the roll rings used in the finishing rolling units of high – speed wire – rolling mills.
